PayPal SOAP API Basics
Last updated: Sept 18th, 5:44pm
Important: NVP/SOAP is a legacy integration method. We accept new integrations and support existing integrations, but there are newer solutions. If you're starting an integration, we recommend our latest solutions.
The PayPal SOAP API is based on open standards known collectively as web services, which include the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP), Web Services Definition Language (WSDL), and the XML Schema Definition language (XSD). A wide range of development tools on a variety of platforms support web services.
Like many web services, PayPal SOAP is a combination of client-side and server-side schemas, hardware and software servers, and core services.
PayPal SOAP High-level Diagram
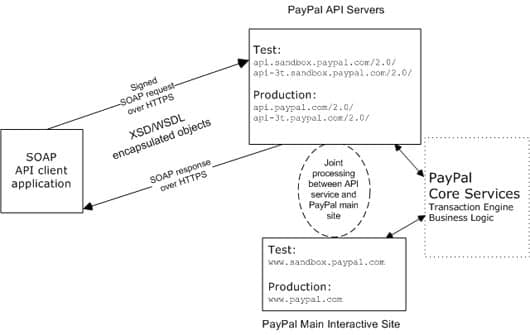
In an object-oriented processing model, the interface to SOAP requests/responses is an object in your application's native programming language. Your third-party SOAP client generates business-object interfaces and network stubs from PayPal-provided WSDL and XSD files that specify the PayPal SOAP message structure, its contents, and the PayPal API service bindings. A business application works with data in the form of object properties to send and receive data by calling object methods. The SOAP client handles the details of building the SOAP request, sending it to the PayPal service, and converting the response back to an object.
PayPal WSDL/XSD Schema Definitions
The PayPal Web Services schema and its underlying eBay Business Language (eBL) base and core components are required for developing applications with the PayPal Web Services API. The following are the locations of the WSDL and XSD files.
| Development and Testing with the PayPal sandbox | |
|---|---|
| PayPal Schema | https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/wsdl/PayPalSvc.wsdl |
| eBL Base Components and Component Types | https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/wsdl/eBLBaseComponents.xsd https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/wsdl/CoreComponentTypes.xsd |
| Production with the Live PayPal API | |
| PayPal Schema | https://www.paypal.com/wsdl/PayPalSvc.wsdl |
| eBL Base Components and Component Types | https://www.paypal.com/wsdl/eBLBaseComponents.xsd https://www.paypal.com/wsdl/CoreComponentTypes.xsd |
PayPal SOAP API Definitions
The PayPal SOAP API comprises individual API definitions for specific business functions. As a foundation, the API relies on eBay Business Language (eBL) base and core components. The core eBL structures AbstractRequestType and AbstractResponseType are the basis of the SOAP request and response of each PayPal API. AbstractResponseType is also the framework for error messages common across all PayPal APIs.
PayPal has made some schema design decisions that can affect how businesses design their own applications.
- Enumerations — Enumerations are defined directly in the PayPal API schema.
- Troubleshooting information — The PayPal API returns information about elements that trigger errors.
- Backward compatibility — The PayPal API is versioned so that business applications are backward compatible when new elements are introduced to the server-side schema.
Note: eBL defines many structures that are specific to processing auctions. PayPal's SOAP schema includes these definitions to maintain compatibility with eBay's SOAP. The material focuses only on those SOAP definitions pertinent to use of the PayPal SOAP API.
Security
The PayPal SOAP API service is protected to ensure that only authorized PayPal members use it. There are four levels of security:
-
A required API
Usernameand APIPassword. -
A third required authentication mechanism, which is either one of the following:
- Client-side request signing using a PayPal-issued API Certificate
- Request authentication using an API Signature included in the request
-
If you're calling the API on behalf of a third-party merchant, you must specify the email address on file with PayPal of the third-party merchant or the merchant's account ID (sometimes called Payer ID) in the
Subjectfield.Note: Third-parties can obtain their merchant ID by logging in to paypal.com, clicking the profile icon on the top right side of the page and then selecting Profile and settings in the Business Profile menu. (If the profile icon at the top of the page is not visible, click Profile, which appears in the top menu when the My Account tab is selected.) Click My business info on the left, and the Merchant account ID is displayed in the list of profile items on the right.
Typically, a merchant grants third-party permissions to a shopping cart, so the shopping cart can call the API on the merchant's behalf. The merchant must have previously granted you permission to execute the API operation.
-
Transport Layer Security (TLS) data transport. See the PayPal developer Information Security guidelines for more information on TLS.
A failure of authenticated security at any one of these levels denies access to the PayPal SOAP API service.
SOAP RequesterCredentials: Username, Password, Signature, and Subject
For the security of your business, PayPal must verify that merchants or third-party developers are permitted to initiate a transaction before they make one. PayPal authenticates each request. If the request cannot be authenticated, a SOAP security fault is returned.
In the SOAP request header, your SOAP client must set the Username, Password elements to pass an API username/password combination. In addition, you can set the Signature to specify your API signature string. If you're calling the API on behalf of a third-party merchant, you must set the Subject element to specify the authorizing third-party's email address or merchant account ID (sometimes called Payer ID).
Note: Third-parties can obtain their merchant ID by logging in to paypal.com, clicking the profile icon on the top right side of the page and then selecting Profile and settings in the Business Profile menu. (If the profile icon at the top of the page is not visible, click Profile, which appears in the top menu when the My Account tab is selected.) Click My business info on the left, and the Merchant account ID is displayed in the list of profile items on the right.
Typically, a merchant grants third-party permissions to a shopping cart, so the shopping cart can call the API on the merchant's behalf. The merchant must have previously granted you permission to execute the API operation.
The following example shows part of the RequesterCredentials elements.
Most of these elements are required for all SOAP requests.
1<SOAP-ENV:Header>2 <RequesterCredentials xmlns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI" xsi:type="ebl:CustomSecurityHeaderType">3 <Credentials xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents" xsi:type="ebl:UserIdPasswordType">4 <Username><var>API-Username</var></Username>5 <Password><var>API-Password</var></Password>6 <Signature><var>API-Signature</var></Signature>7 <Subject><var>Authorizing-Merchant-Email</var> -or- <var>Authorizing-Merchant-Account-ID</var></Subject>8 </Credentials>9 </RequesterCredentials>10</SOAP-ENV:Header>
| Element | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
Username |
API-Username |
Your API username, which is auto-generated by PayPal when you apply for certificate or signature API credentials to use the PayPal SOAP API. You can see this value on https://www.paypal.com/ in your Profile under API Access > API Credentials. |
Password |
API-Password |
Your API password, which you specify when you apply for certificate or signature API credentials to use the PayPal SOAP API. |
Signature |
API-Signature |
Your API signature, if you use one instead of an API Certificate. |
Subject |
Authorizing-Merchant-Email
or Authorizing-Merchant-Account-ID
|
The email address or merchant account ID (sometimes called Payer ID) of a third-party for whom you are sending requests to the PayPal SOAP API. Your API username must have been granted permission by this third-party to make a PayPal API request on its behalf. |
SOAP Service Endpoints
The service endpoint that processes your SOAP requests depends on your API credentials type.
| API Credentials Type | Live Production Endpoint | Test (Sandbox) Endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| API Certificate | https://api.paypal.com/2.0/ | https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/2.0/ |
| API Signature | https://api-3t.paypal.com/2.0/ | https://api-3t.sandbox.paypal.com/2.0/ |
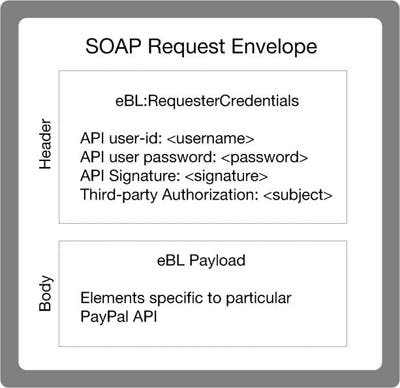
SOAP Request Envelope
The following diagram illustrates the contents of a PayPal SOAP request envelope.
All PayPal APIs are based on two core structures: AbstractRequestType and AbstractResponseType.
Diagram of the SOAP Request Envelope
Request Structure
The following annotated description of the SOAP request structure shows the elements required by the PayPal SOAP API.
General Structure of PayPal API SOAP Request
11. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>22. <SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"3 xmlns:SOAP-ENC="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/"4 xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"5 xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" SOAP-ENV:encodingStyle="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/">63. <SOAP-ENV:Header>74. <RequesterCredentials xmlns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI">85. <Credentials xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">96. <Username>API-Username</Username>107. <Password>API-Password</Password>118. <Signature/>129. <Subject/>1310. </Credentials>1411. </RequesterCredentials>1512. </SOAP-ENV:Header>1613. <SOAP-ENV:Body>1714. <Specific-API-Name-Req xmlns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI">1815. <Specific-API-Name-Request>1916. <Version xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">API-Version</Version>2017. <Required-Or-Optional-Fields xs:type="Type">Data</Required-Or-Optional-Fields>2118. </Specific-API-Name-Request>2219. </Specific-API-Name-Req>2320. </SOAP-ENV:Body>2421. </SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
| Lines | Comment |
|---|---|
| 6, 7 | The Username and Password fields are part of the PayPal SOAP API RequesterCredentials security authentication mechanism you must construct for every SOAP request header. See RequesterCredentials for more information. |
| 8 | The Signature element should include your API Signature if that is the type of API credential you are using. |
| 9 | The Subject element should be included when using third-party permissions (performing transactions on behalf of another merchant who authorized you to do so). Pass the authorizing third-party's merchant account ID (sometimes called Payer ID) or email address. |
| 13 through 20 | The SOAP request for every PayPal API follows this element-naming pattern. The API's specific name is appended with Req, and in this element the Specific-API-Name-Req is nested. Each Specific-API-Name-Request has a corresponding Specific-API-Name-RequestType. |
| 16 | The number of the PayPal SOAP API version is required on each SOAP request. This version number is the value of ns:version in https://www.paypal.com/wsdl/PayPalSvc.wsdl. |
| 17 | For details about required and optional elements and values for specific requests, see the API references. |
SOAP Message Style: doc-literal
PayPal uses doc-literal SOAP messaging, not rpc-encoding. With doc-literal, a single service interface call passes an XML document in the request to the PayPal API server, which responds with an XML document instance.
Response Structure
The following is an annotated description of the structure of a successful SOAP response from the PayPal API where Ack=Success:
11. <?xml version="1.0"?>22. <SOAP-ENV:Envelope3 xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"4 xmlns:SOAP-ENC="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/"5 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"6 xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"7 xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"8 xmlns:cc="urn:ebay:apis:CoreComponentTypes"9 xmlns:wsu="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/utility"10 xmlns:saml="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.0:assertion"11 xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"12 xmlns:wsse="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/12/secext"13 xmlns:ebl="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents"14 xmlns:ns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI">153. <SOAP-ENV:Header>164. <Security xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/12/secext"xsi:type="wsse:SecurityType"/>175. <RequesterCredentials xmlns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI" xsi:type="ebl:CustomSecurityHeaderType">186. <Credentials xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents" xsi:type="ebl:UserIdPasswordType"/>197. </RequesterCredentials>208. </SOAP-ENV:Header>219. <SOAP-ENV:Body id="_0">2210. <<var>Specific-API-Operation-Name>-Response xmlns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI">2311. <Timestamp xmlns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI"><var>DateTime-In-UTC/GMT-Format</var></TIMESTAMP>2412. <Ack xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">Success</Ack>2513. <Version xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents"><var>API-Version</var></Version>2614. <CorrelationId xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents"><var>Correlation-ID</var></CorrelationID>2715. <Build xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents"><var>API-Build-Number</var></Build>2816. <<var>Elements-For-Specific-API-Response</var>><data></<var>Elements-For-Specific-API-Response</var>>2917. </<var>Specific-API-Operation-Name-Response>3018. </SOAP-ENV:Body>3119. </SOAP-ENV:Envelope>32</var></data></var>
| Lines | Comment |
|---|---|
| 10 - 17 | The Specific-API-Operation-Name-Response start and end elements. An example of an API operation is SetExpressCheckout. See the NVP/SOAP API reference for a complete list. |
| 11 | Each API response contains a Timestamp with its date and time in UTC/GMT format. |
| 12 | The acknowledgment (Ack) element contains the string Success indicating the corresponding request was successfully processed. When there's an error, Ack is set to a value other than Success, and the response body contains an Errors element with information to help you troubleshoot the cause of the error. See Error Responses for more information. |
| 14 | The CorrelationID element contains information about the PayPal application that processed the request. Use the value of this element if you need to troubleshoot a problem with one of your requests. |
| 16 | The different PayPal APIs return different elements depending on their response definitions. For detailed information, see the descriptions in the API reference. Note: Because a field is defined in the formal structure of an API response, this does not mean that the field is necessarily returned. Data is returned in a response only if PayPal has recorded data that corresponds to the field. |
Error Responses
If the Ack value is not Success, the payment or desired action may not go through.
Possible values of the Ack response field are the following:
Success— The request was successful.SuccessWithWarning— The request was successful but a warning error code was also returned.Failure— The API request failed. See error messages for details.FailureWithWarning— The API request failed and additional warning messages were returned.
If a request is malformed or contains some other error, the body of the SOAP response contains an Errors element with other elements that can help you troubleshoot the cause of the error.
The structure of error messages is as follows:
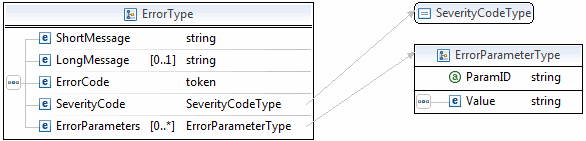
The most important of these additional elements are as follows:
ShortMessageLongMessageErrorCode
Additional information can appear as part of ErrorParametersType. For example, if the response returned within the ParamID element is ProcessorResponse, the Value element would contain a third-party card processor's specific error, such as 0091. Values set in the ErrorParametersType are not set by PayPal; rather, they are passed through from the source.
Note: PayPal only passes selected values in ErrorParametersType.
The following example shows the error response if your API username and password do not match a legitimate API username and password on file with PayPal.
Example of the SOAP Error Response: Bad Username or Password
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>2<SOAP-ENV: Envelope [DETAILS NOT SHOWN]>3 <SOAP-ENV:Header>[DETAILS NOT SHOWN]</SOAP-ENV:Header>4 <SOAP-ENV:Body id="_0">5 <GetTransactionDetailsResponse xmlns="urn:ebay:api:PayPalAPI">6 <Timestamp xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">2005-02-09T21:51:26Z</Timestamp>7 <Ack xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">Failure</Ack>8 <Errors xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents" xsi:type="ebl:ErrorType">9 <ShortMessage xsi:type="xs:string">Authentication/Authorization Failed</ShortMessage>10 <LongMessage xsi:type="xs:string">Username/Password is incorrect</LongMessage>11 <ErrorCode xsi:type="xs:token">10002</ErrorCode>12 <SeverityCode xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">Error</SeverityCode>13 </Errors>14 <CorrelationID xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents"><var>Debugging-Info</var></CorrelationID>15 <Version xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">124.00</Version>16 <Build xmlns="urn:ebay:apis:eBLBaseComponents">1.0006</Build>17 <...other elements="" in="" response...="">18 </SOAP-ENV:Body>19</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>20</...other>
CorrelationID for Reporting Problems to PayPal
The value returned in CorrelationID is important for PayPal to determine the precise cause of any error you might encounter. If you have to troubleshoot a problem with your requests, we suggest that you capture the value of CorrelationID so you can report it to PayPal.
UTF-8 Character Encoding
The PayPal API assumes that all data in requests is in Unicode, specifically, the Unicode (or UCS) Transformation Format, 8-bit encoding form (UTF-8).
In responses, the API always returns data in UTF-8.
Date/Time Formats
The PayPal SOAP API schema defines date/time values as Coordinated Universal Time (UTC/GMT), using ISO 8601 format, and of type ns:dateTime.
An example date/time stamp is 2006-08-24T05:38:48Z
Core Currency Amount Data Type
The core currency amount data type is called BasicAmountType and is derived from string. All currency amount fields have the following structure:
- The
currencyIDattribute is required. - The amount must have two decimal places, except in the case of currencies that do not support decimal amounts.
- The decimal separator must be a period (".").
- You must not use any thousands separator.
BasicAmountTypehas a data type ofebl:CurrencyCodeType, which defines a large number of different currency codes. However, for your processing to succeed, you must set currencyCode to a valid currency code.
Example
The field name, Amount, is an example; actual field names can vary depending on the specific API operation.
1<Amount currencyCode="USD">3.00</Amount>